Java Multidimensional Arrays
Before we learn about the multidimensional array, make sure you know about Java array.
A multidimensional array is an array of arrays. Each element of a multidimensional array is an array itself. For example,
int[][] a = new int[3][4];
Here, we have created a multidimensional array named a. It is a 2-dimensional array, that can hold a maximum of 12 elements,
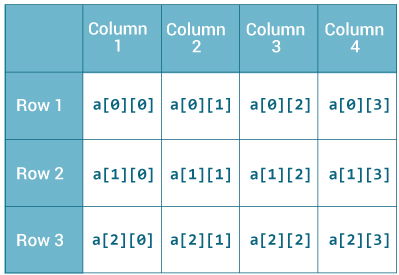
Remember, Java uses zero-based indexing, that is, indexing of arrays in Java starts with 0 and not 1.
Let’s take another example of the multidimensional array. This time we will be creating a 3-dimensional array. For example,
String[][][] data = new String[3][4][2];
Here, data is a 3d array that can hold a maximum of 24 (3*4*2) elements of type String.
How to initialize a 2d array in Java?
Here is how we can initialize a 2-dimensional array in Java.
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};As we can see, each element of the multidimensional array is an array itself. And also, unlike C/C++, each row of the multidimensional array in Java can be of different lengths.

Example: 2-dimensional Array
class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a 2d array
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};
// calculate the length of each row
System.out.println("Length of row 1: " + a[0].length);
System.out.println("Length of row 2: " + a[1].length);
System.out.println("Length of row 3: " + a[2].length);
}
}Output:
Length of row 1: 3 Length of row 2: 4 Length of row 3: 1
In the above example, we are creating a multidimensional array named a. Since each component of a multidimensional array is also an array (a[0], a[1] and a[2] are also arrays).
Here, we are using the length attribute to calculate the length of each row.
Example: Print all elements of 2d array Using Loop
class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = {
{1, -2, 3},
{-4, -5, 6, 9},
{7},
};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < a[i].length; ++j) {
System.out.println(a[i][j]);
}
}
}
}Output:
1 -2 3 -4 -5 6 9 7
We can also use the for…each loop to access elements of the multidimensional array. For example,
class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a 2d array
int[][] a = {
{1, -2, 3},
{-4, -5, 6, 9},
{7},
};
// first for...each loop access the individual array
// inside the 2d array
for (int[] innerArray: a) {
// second for...each loop access each element inside the row
for(int data: innerArray) {
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}
}Output:
1 -2 3 -4 -5 6 9 7
In the above example, we are have created a 2d array named a. We then used for loop and for...each loop to access each element of the array.
How to initialize a 3d array in Java?
Let’s see how we can use a 3d array in Java. We can initialize a 3d array similar to the 2d array. For example,
// test is a 3d array
int[][][] test = {
{
{1, -2, 3},
{2, 3, 4}
},
{
{-4, -5, 6, 9},
{1},
{2, 3}
}
};Basically, a 3d array is an array of 2d arrays. The rows of a 3d array can also vary in length just like in a 2d array.
Example: 3-dimensional Array
class ThreeArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a 3d array
int[][][] test = {
{
{1, -2, 3},
{2, 3, 4}
},
{
{-4, -5, 6, 9},
{1},
{2, 3}
}
};
// for..each loop to iterate through elements of 3d array
for (int[][] array2D: test) {
for (int[] array1D: array2D) {
for(int item: array1D) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
}
}
}Output:
1 -2 3 2 3 4 -4 -5 6 9 1 2 3